

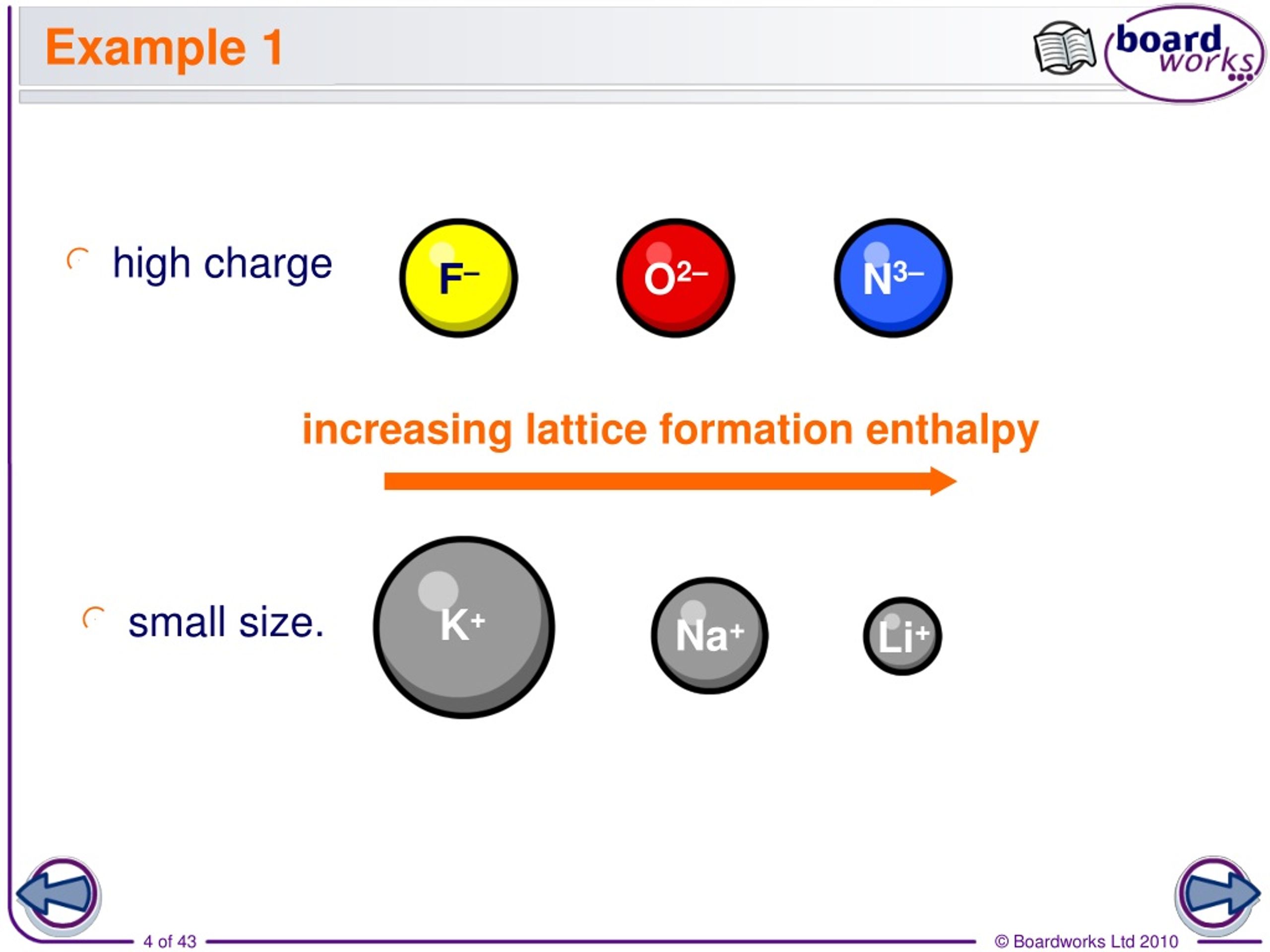
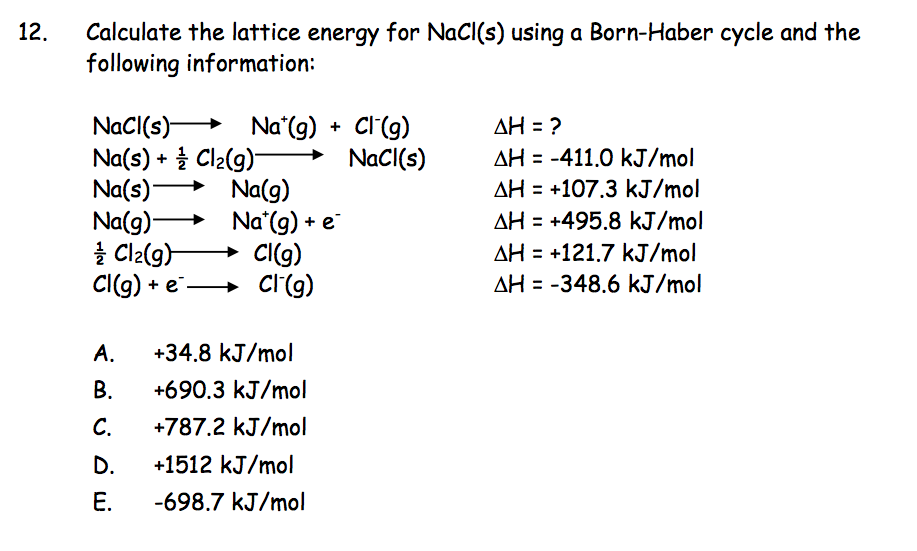
For example, the lattice energy of NaCl is larger than the lattice energy of KCl. Lattice energies are large when ions are closer together, the distance between the ions is small and when the charges are larger. Coulomb’s law is equal to a constant, k, multiplied by the product of the ion charges, z 1 and z 22, between the ions. Recall, lattice energy is positive meaning it is endothermic. The stronger the bond, the higher the lattice energy. Lattice energy, E lattice is dependent on the strength of the bond between the cation and anion in an ionic bond. The lattice energy is always positive, because it takes energy to separate the ions from the solid. The equation for the lattice energy is the reverse of the equation in Step 5 in the figure below, for the formation of the solid from its ions which releases 787 kJ/mol of energy.Ī Born-Haber cycle allows the calculation of the lattice energy for a solid ionic compound. The process absorbs energy, and is highly endothermic. The Born-Haber Cycle is essentially Hess's Law applied to an ionic solid.Lattice energy, E lattice is the energy required to separate one mole of a solid ionic compound into its gaseous ions.
Ionization Energy is the energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom or an ion.There are several important concept to understand before the Born-Haber Cycle can be applied to determine the lattice energy of an ionic solid ionization energy, electron affinity, dissociation energy, sublimation energy, heat of formation, and Hess's Law. Some require such high temperatures that they decompose before they can reach a melting and/or boiling point. It is this that causes ionic solids to have such high melting and boiling points. A lot of energy is released as the oppositely charged ions interact. However, the crystalline structure allows each ion to interact with multiple oppositely charge ions, which causes a highly favorable change in the enthalpy of the system. Some might expect such an ordered structure to be less stable because the entropy of the system would be low. Lattice Energy is used to explain the stability of ionic solids.
Its values are usually expressed with the units kJ/mol. As implied in the definition, this process will always be exothermic, and thus the value for lattice energy will be negative. The other definition says that lattice energy is the reverse process, meaning it is the energy released when gaseous ions bind to form an ionic solid. This definition causes the value for the lattice energy to always be positive, since this will always be an endothermic reaction. In one definition, the lattice energy is the energy required to break apart an ionic solid and convert its component atoms into gaseous ions. Lattice Energy is a type of potential energy that may be defined in two ways.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
